 Gene: BRCA2
Gene: BRCA2
Cancer Risks and Management (per NCCN version 3.2019):
Women:
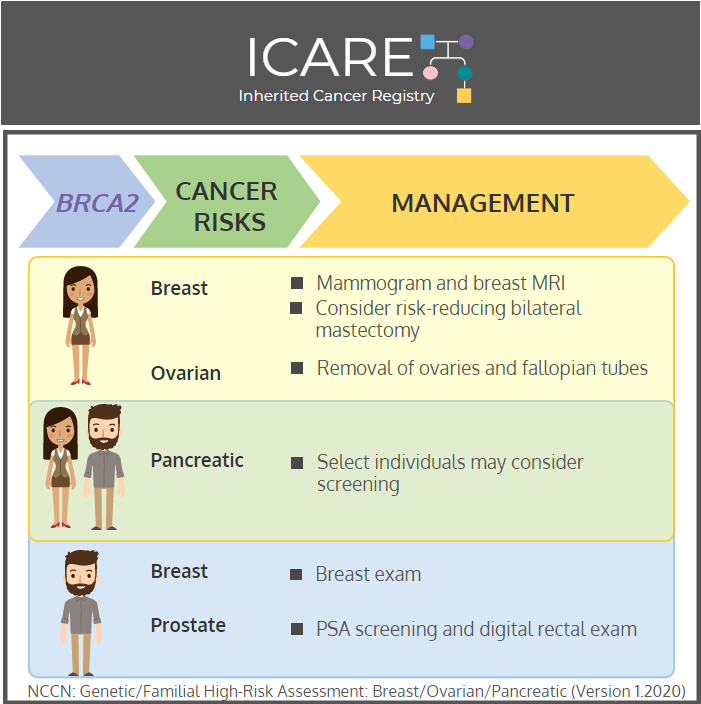
Breast cancer risk: Elevated at 60%-70% – Recommend clinical breast exam every 6-12 months starting at age 25, annual breast MRI with contrast starting at age 25, and annual mammogram with consideration of tomosynthesis starting at age 30; consider risk-reducing mastectomy.
Ovarian cancer risk: Up to 27% – Recommend risk-reducing bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (removal of ovaries and fallopian tubes) between ages 40 and 45.
Men and Women:
Pancreatic cancer risk: Elevated – Consider MRI/MRCP or endoscopic ultrasound for BRCA2 carriers with a family history of pancreatic cancer in first-degree relative.
Men:
Breast cancer risk: Breast cancer risk: Elevated at 6%-8% – Recommend annual clinical breast exams starting at age 35.
Prostate cancer risk: Up to 20% – Recommend PSA screening and digital rectal exam starting at age 40.
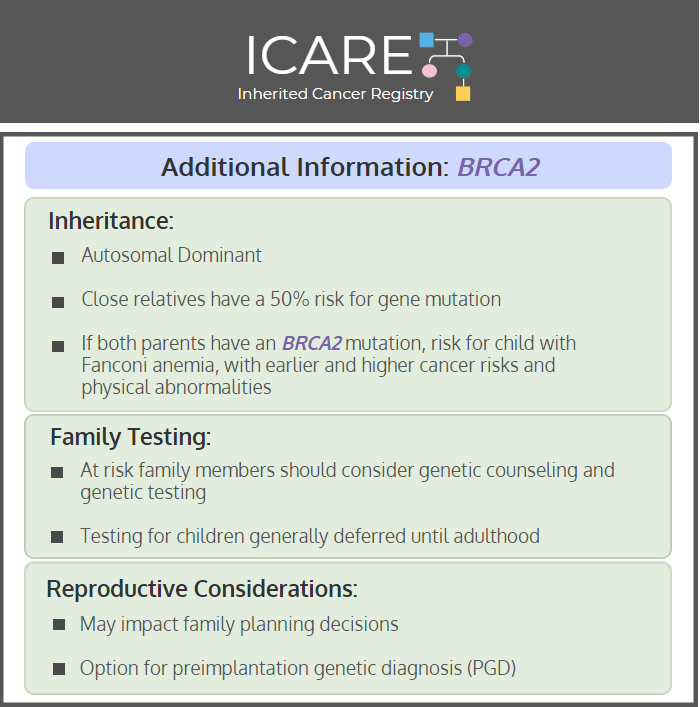
Inheritance: Autosomal dominant, thus parents, full siblings, and children have a 50% risk for the gene mutation. If both parents have a BRCA2 mutation, the child is at risk for autosomal recessive Fanconi anemia.
Family Testing: At-risk family members should consider genetic counseling and genetic testing. For adult-onset conditions, recommend waiting to perform genetic testing on minors are at least 18 years old.
Reproductive Considerations: Option for preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) may be available to ensure future generations do not inherit the known gene mutation. PGD is a procedure available for certain gene mutations to screen the embryo prior to achievement of pregnancy.
Check out the full management guidelines by creating a FREE account at https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/genetics_bop.pdf
