𝗚𝗲𝗻𝗲: 𝗔𝗣𝗖
Cancer Risks and Management per National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Colorectal Version 1.2020
𝗠𝗲𝗻 & 𝗪𝗼𝗺𝗲𝗻:
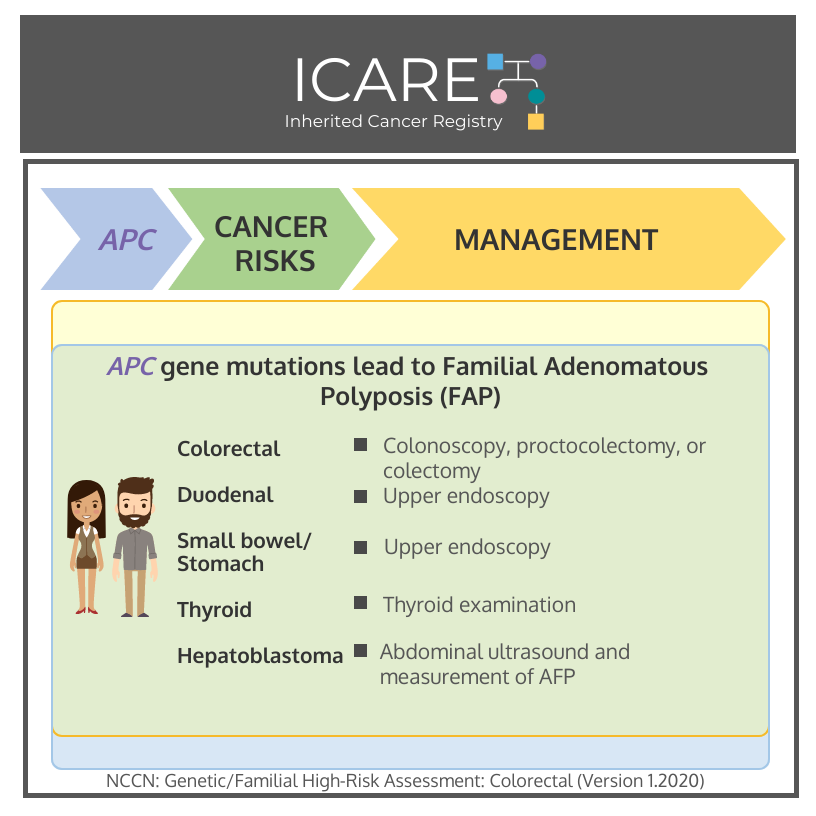
𝘈𝘗𝘊 mutation leading to classic form of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP):
Colorectal cancer risk: >99% if untreated – Treatment is based on polyp burden and includes proctocolectomy (with subsequent endoscopic screening of the ileal pouch) or colectomy (with subsequent screening of the rectum).
Attenuated FAP (a less serious form of FAP, compared to classic FAP):
Colorectal cancer risk: Elevated to 70% – Recommend colonoscopy every 1-2 years; Treatment is based on polyp burden and may include polypectomy or colectomy.
Intra-abdominal desmoid tumor risk: Elevated – Recommend physical exam with consideration of screening through MRI or CT.
Stomach, small bowel (particularly duodenal), and periampullary cancer and polyp risks: Elevated – Recommend upper endoscopy.
Pancreatic cancer risk: Elevated – No screening recommendations at this time.
Thyroid cancer risk: Elevated – Recommend physical examination and ultrasound.
Hepatoblastoma risk: Elevated – Consider physical exam, abdominal ultrasound and AFP levels in first 5 years of life.
Central nervous system cancer risk: Recommend physical examination.
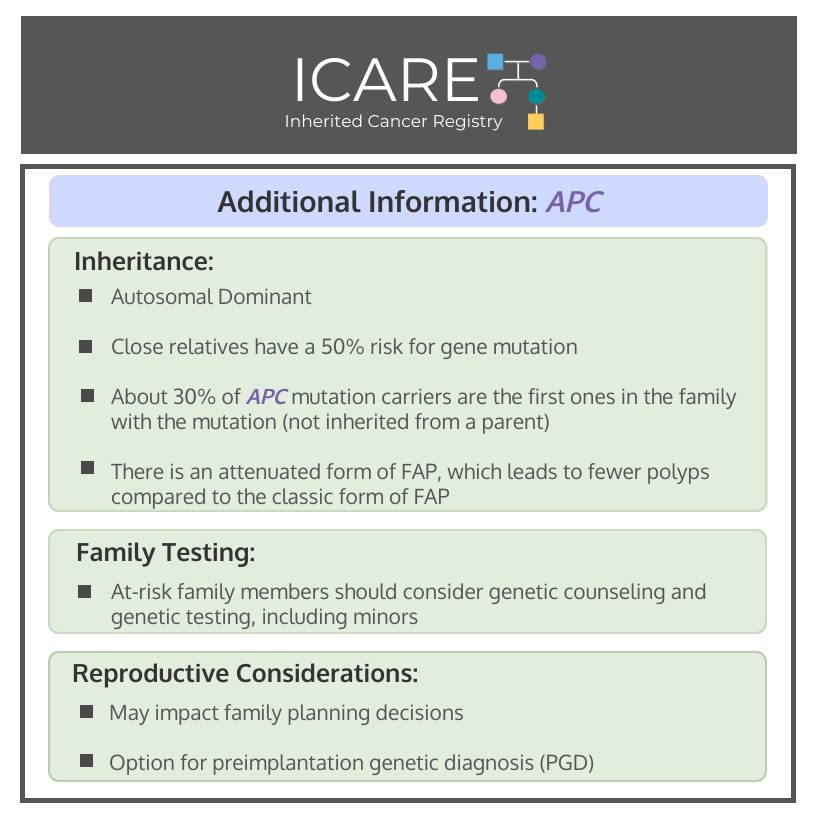
Inheritance: Autosomal dominant; thus, parents, full siblings, and children have a 50% risk for the gene mutation. About 30% of individuals with an 𝘈𝘗𝘊 mutation are the first in the family with the mutation, meaning they most likely did not inherit the mutation from a parent and risk to other relatives is low. There is an attenuated form of FAP, which leads to fewer polyps compared to the classic form of FAP.
Family Testing: At-risk family members should consider genetic counseling and testing.
Reproductive Considerations: Option for preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) may be available to ensure future generations do not inherit the known gene mutation. PGD is a procedure available for certain gene mutations to screen the embryo prior to achievement of pregnancy.
Check out the full management guidelines by creating a 𝗙𝗥𝗘𝗘 account at https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/genetics_colon.pdf
